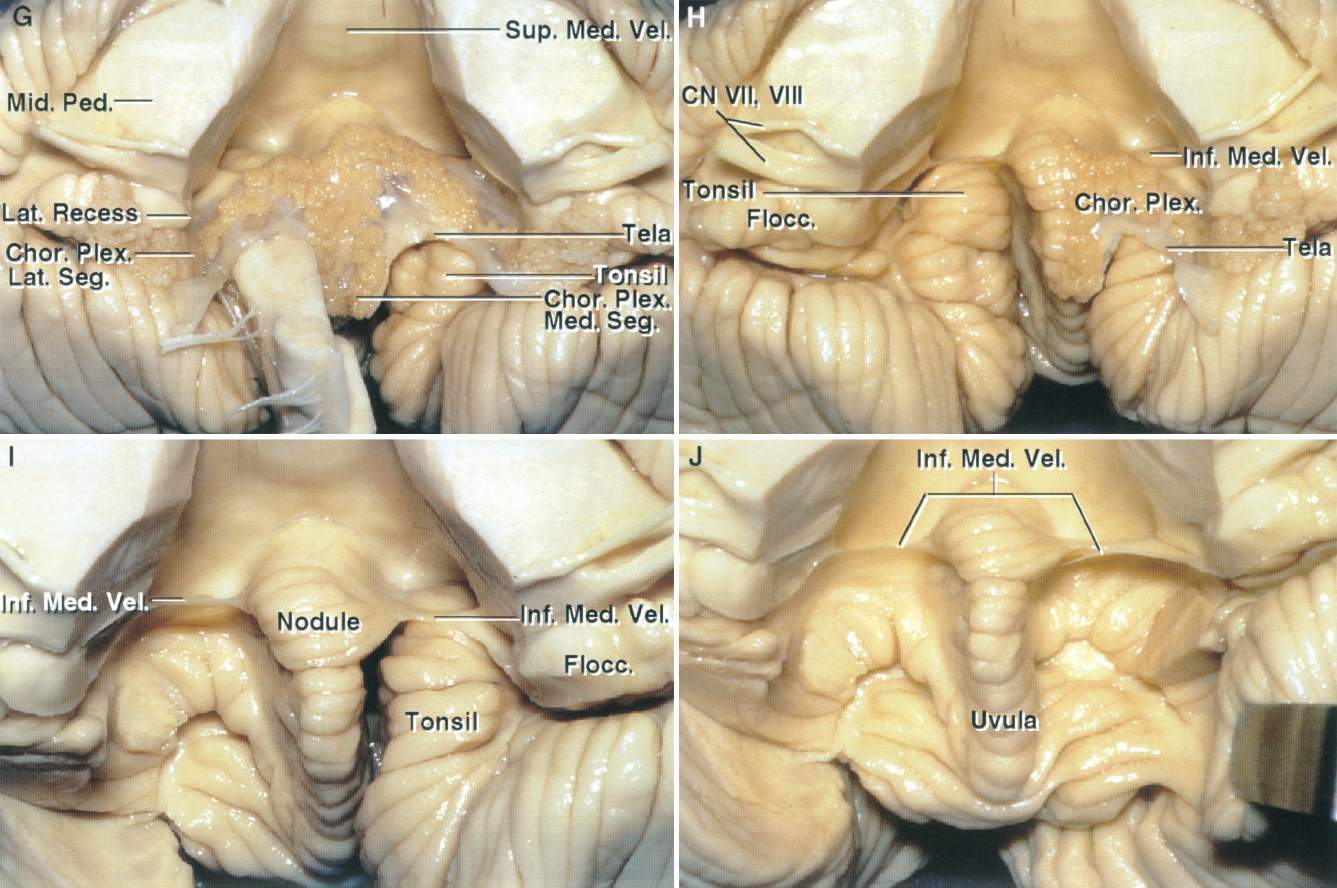
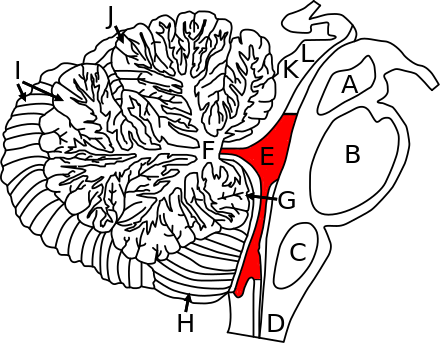
In contrast to the superior roof the inferior roof of the fourth ventricle is formed mainly by two thin membranes the tela choroidea and the inferior medullary velum.
Fourth ventricle roof formation.
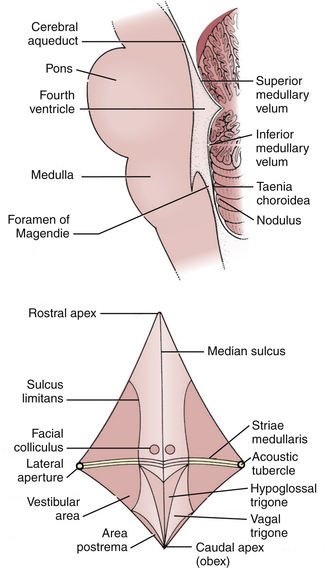
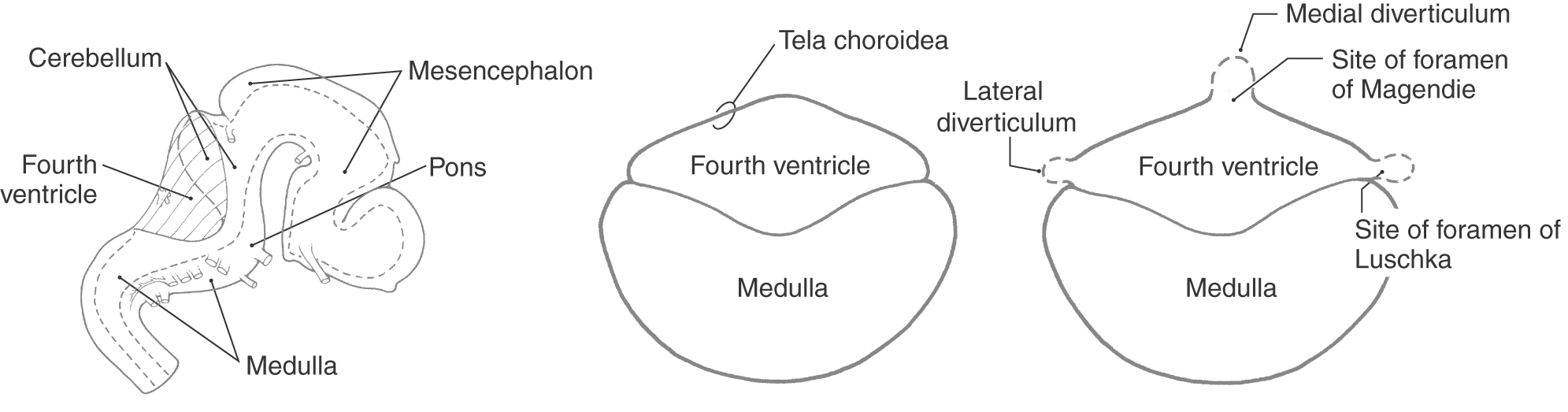
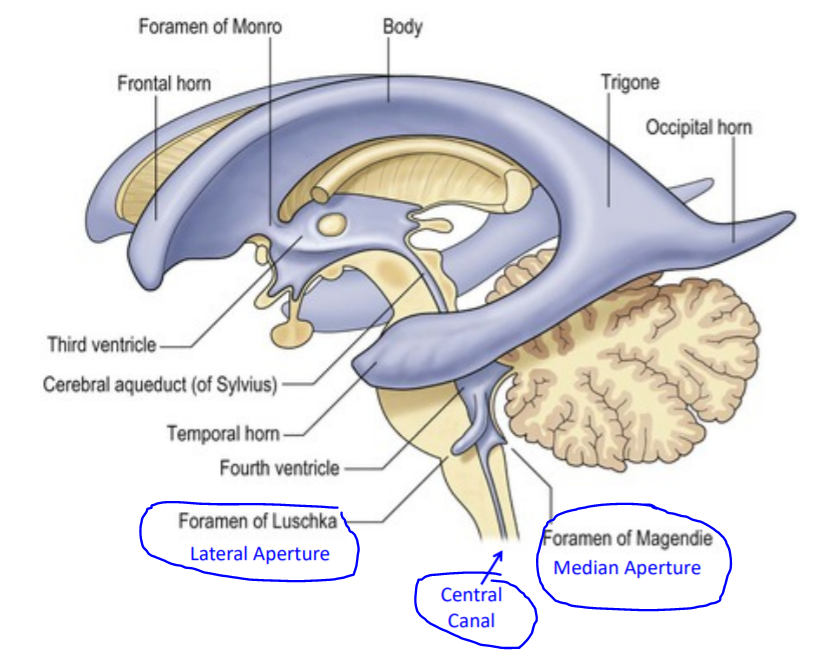
Csf produced and or flowing into the fourth ventricle can exit to the subarachnoid space through lateral apertures and a single median aperture located in the inferiorportion of the roof.
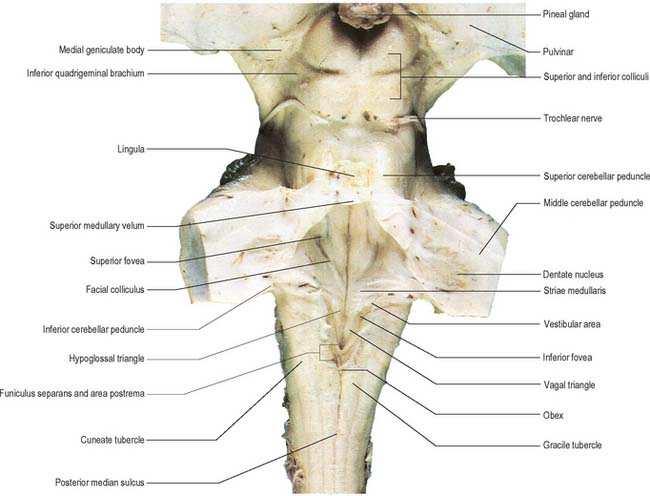
Specifically it spans from the obex an area in the medulla.
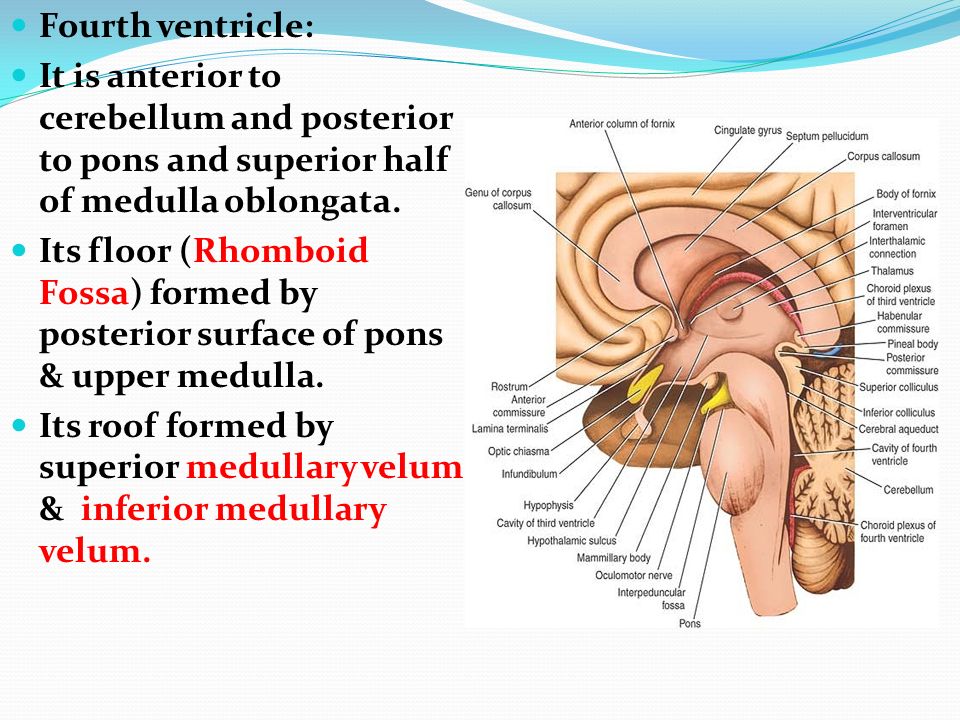
The roof of the 4th ventricle is tent shaped and has upper and lower sloping surfaces.
Just behind its outer surface is the lingula the.
Hypothalamic or thalamic stimulation that depresses reticular formation activity in the brain stem results in.
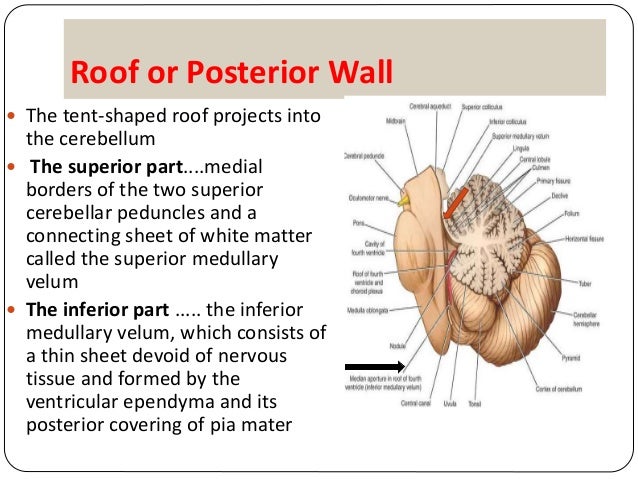
The upper portion of the roof is formed by the cerebellum.
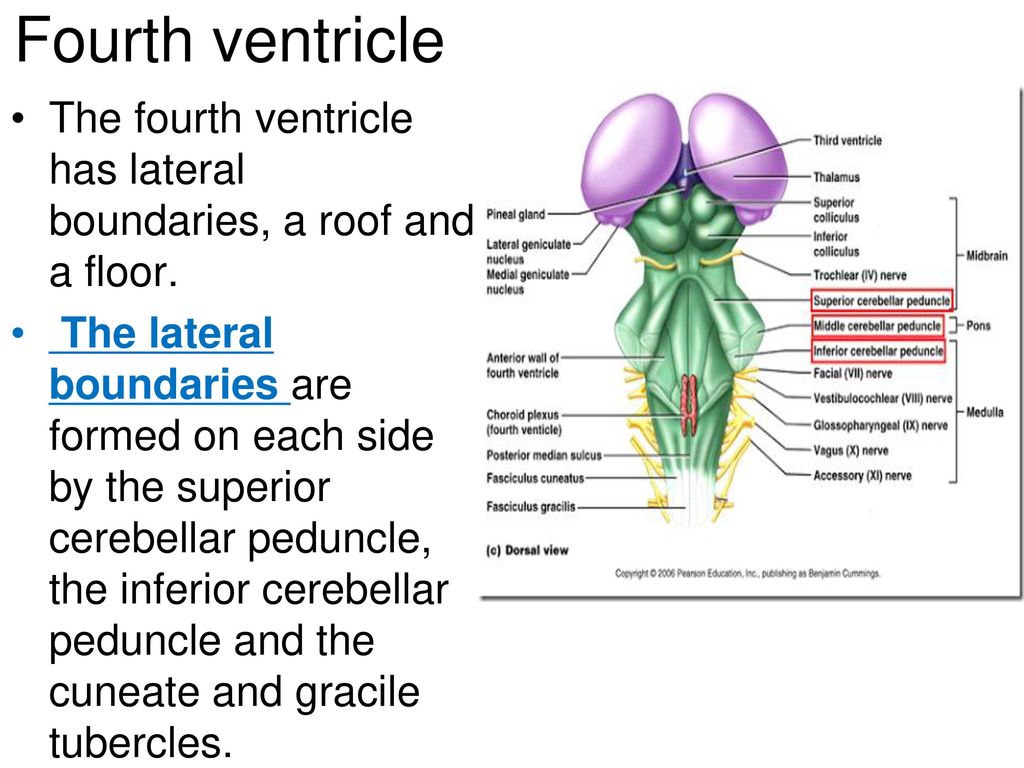
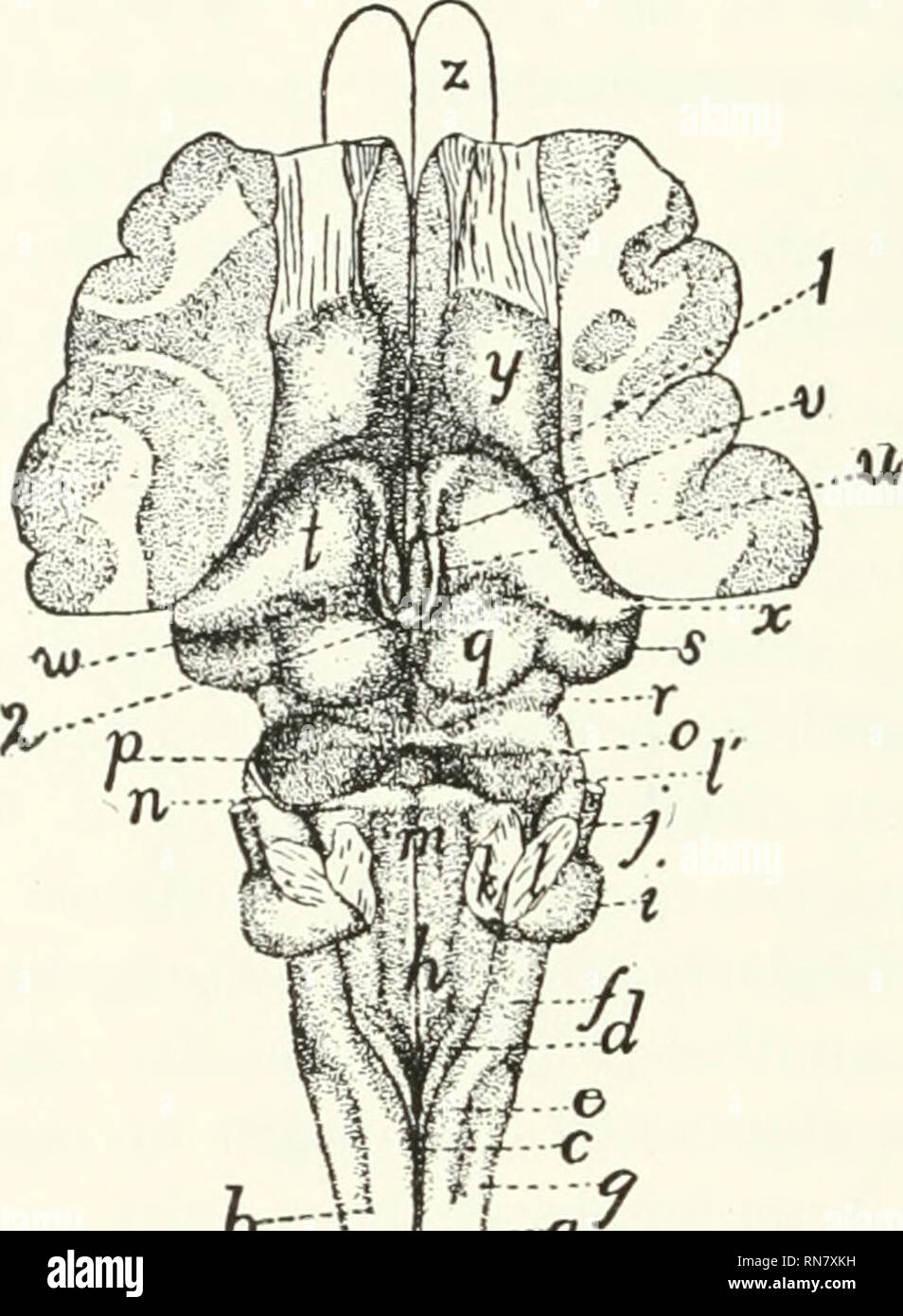
The roof of fourth ventricle is the dorsal surface of the fourth ventricle.
The upper part of the roof is composed by a thin sheet of white matter the superior medullary velum that stretches between both superior cerebellar peduncles.
It has a diamond shape and is located in the upper portion of the medulla.
The roof of ventricle is diamond shaped and can be divided into superior and inferior parts.
Both the squamous roof plate and columnar neuroepithelium can be visualized in live embryos of the cdh2 cdh2 tft reporter line and we followed the progress of ventricle expansion and roof plate formation from 18 hpf in a dorsal view using time lapse confocal microscopy figure 1 video 1.
The roof of the fourth ventricle is tent shaped rising to an apex called the fastigium that divides the superior roof from the inferior roof.
The apex of the tent goes posteriorly into the white core of the cerebellum.
The obex is also a.
Generalized lethargy or actual sleep the slender lobe situation between the roof of the fourth ventricle and cellebelar hemisphere is known as.
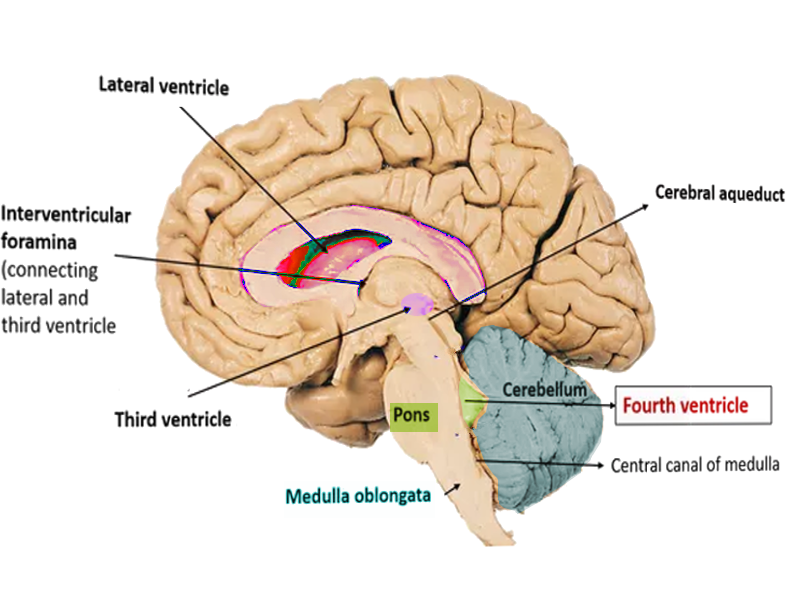
The fourth ventricle contains cerebrospinal fluid.
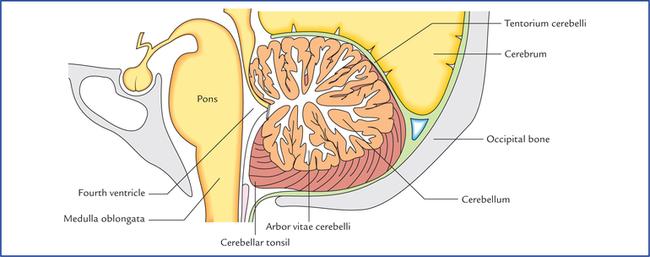
It corresponds to the ventral surface of the cerebellum.
Inferior roof of the fourth ventricle.
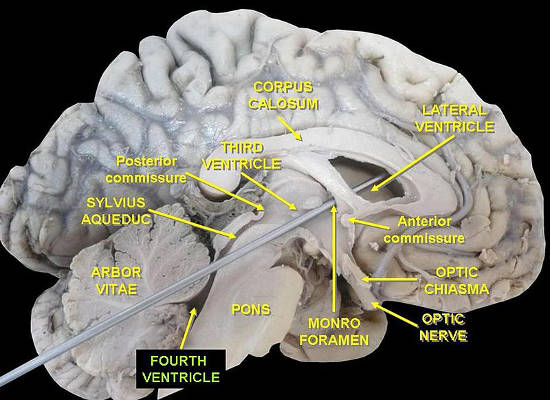
From the third ventricle it flows downward along the aqueduct of sylvius into the fourth ventricle where still another minute amount of fluid is added.
The caudal tip of the fourth ventricle where it becomes the central canal is known as the obex.
Along with the ventricular cavity the roof plate.
Finally the fluid passes out of the fourth ventricle through three small openings two lateral foramina of luschka and a midline foramen of magendie entering the cisterna magna a fluid.
The median part of the superior roof called the superior medullary velum consists of a thin lamina of white matter between the cerebellar peduncles.








:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13983/IxIebEKGr4ReRbXGlvvmhg_Ventriculus_quartus_01.png)




















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/5425/fohUtpnmOo2z6C26IHO4rQ_choroid_plexus_of_the_fourth_ventricle_.png.jpeg)

:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/cranial-nerve-nuclei/eQBBsjAWg0hPPdNKLDnIA_brainstem-and-related-structures_english.jpg)
